
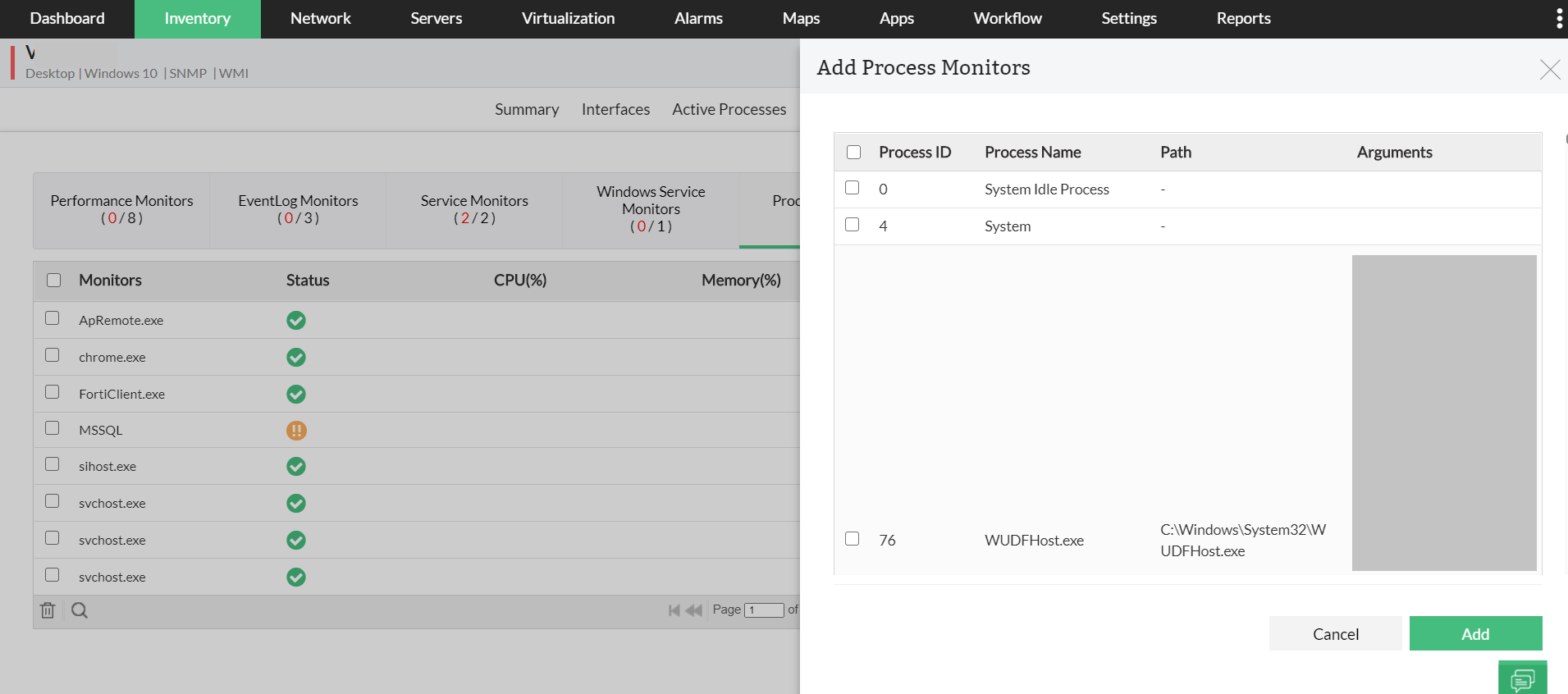
The Processes tab divides the process into three categories:
There are more columns that can be shown. By default the processes tab shows the user account the process is running under, the amount of CPU, and the amount of memory the process is currently consuming. The Delete key can also be used to terminate processes on the Processes tab. This list includes Windows Services and processes from other accounts. The Processes tab shows a list of all running processes on the system. Issuing an end task causes a request for graceful exit to be sent to the application. Right-clicking any of the applications in the list allows switching to that application or ending the application's task. It has a "more details" hyperlink that activates a full-fledged Task Manager with several tabs. In summary mode, Task Manager shows a list of currently running programs that have a main window. This setting is remembered for that user on that machine.
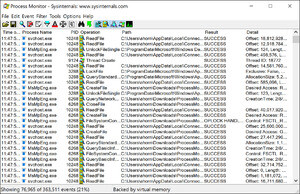
It can be switched to a more detailed mode by clicking More Details. The first time Task Manager is invoked by a user, it shows in a simplified summary mode (described in the user experience as Fewer Details). Task Manager on Windows XP, showing the Processes tab Windows 9x has a program known as Close Program which lists the programs currently running and offers options to close programs as well shut down the computer. Prior versions Windows NT, as well as Windows 3.x, includes the Task List application, is capable of listing currently-running processes and killing them, or creating a new process. Task Manager was introduced in its current form with Windows NT 4.0. The program can be started in recent versions of Windows by pressing ⊞ Win+R and then typing in taskmgr.exe, by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete and clicking Start Task Manager, by pressing Ctrl+⇧ Shift+Esc, or by right-clicking on the Windows taskbar and selecting "Task Manager". Task Manager can also be used to set process priorities, processor affinity, start and stop services, and forcibly terminate processes. It provides information about computer performance and running software, including name of running processes, CPU load, commit charge, I/O details, logged-in users, and Windows services. Manager included with Microsoft Windows systems. Task Manager, previously known as Windows Task Manager, is a task manager, system monitor, and startup


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
